Here below you can find the short list of my publications with abstracts.
List of publications

AGH UST
2018
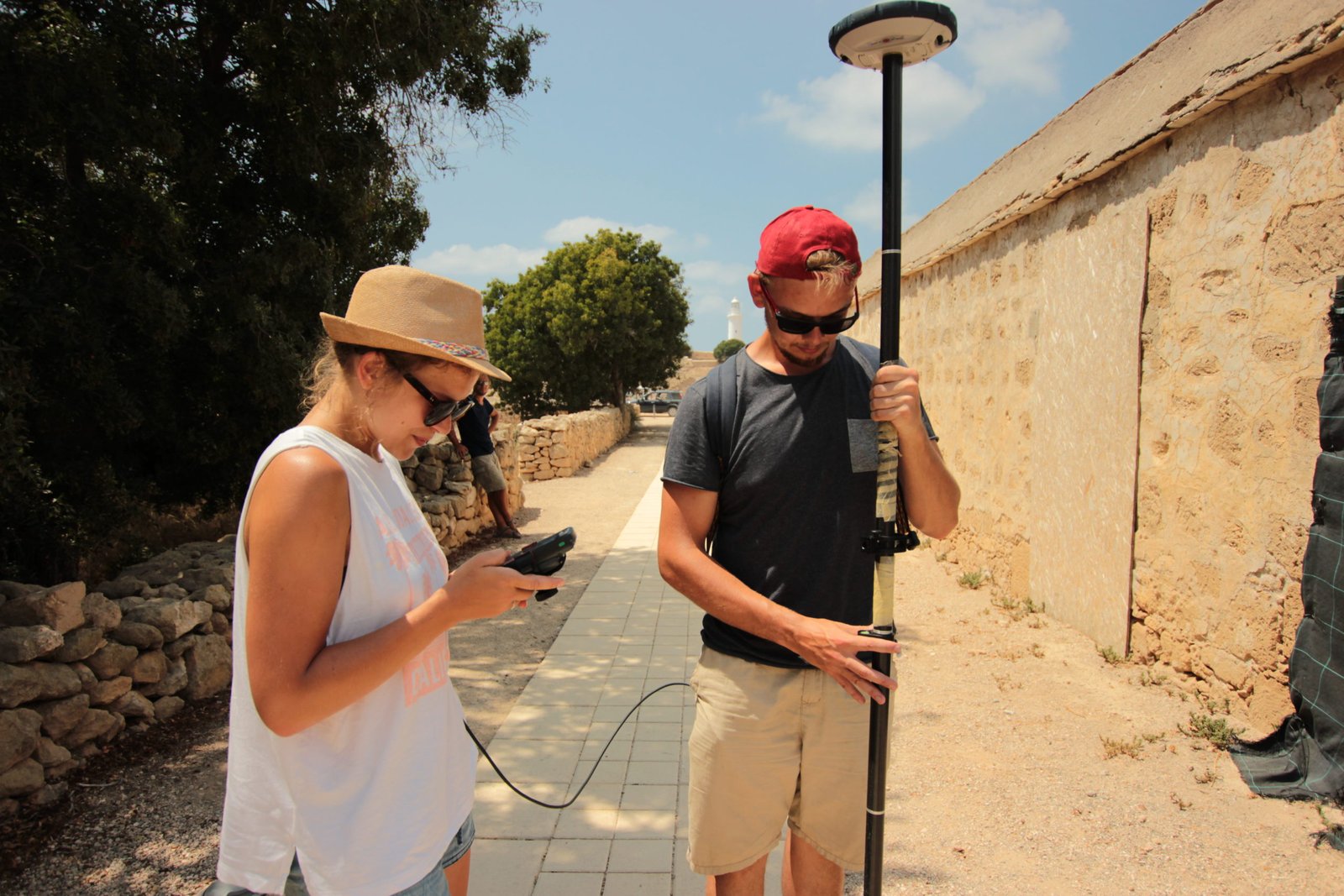
Accuracy evaluation of real-time GNSS precision positioning with RTX Trimble technology
Agnieszka OCHAŁEK, Witold NIEWIEM, Edyta PUNIACH, Paweł ĆWIĄKAŁA
In this paper, authors present results of accuracy verification of the Trimble RTX technology. The GNSS receiver Spectra Precision SP60 was used in Cyprus (Kato Paphos Archaeological Park). To evaluate the accuracy of the receiver, two measuring test networks (consisting of 30 and 55 control points) were established. All points were determined in four measuring cycles. Additionally, in order to make more advanced analysis of the data, the bases were also measured by using another GNSS receiver - Geomax-Zenith 25. The point positions, in this case, were conducted in the local coordinate system of Kato Paphos Archaeological Park by using RTK positioning technology. To make a comparison, it was necessary to transform the coordinates based on different groups of fitting points. Analysis allowed to conclude that the Spectra Precision SP60 receiver and the RTX Trimble technology guarantee repeatable results (on the level of 4 cm) of point positioning measurements.


AGH UST
2017
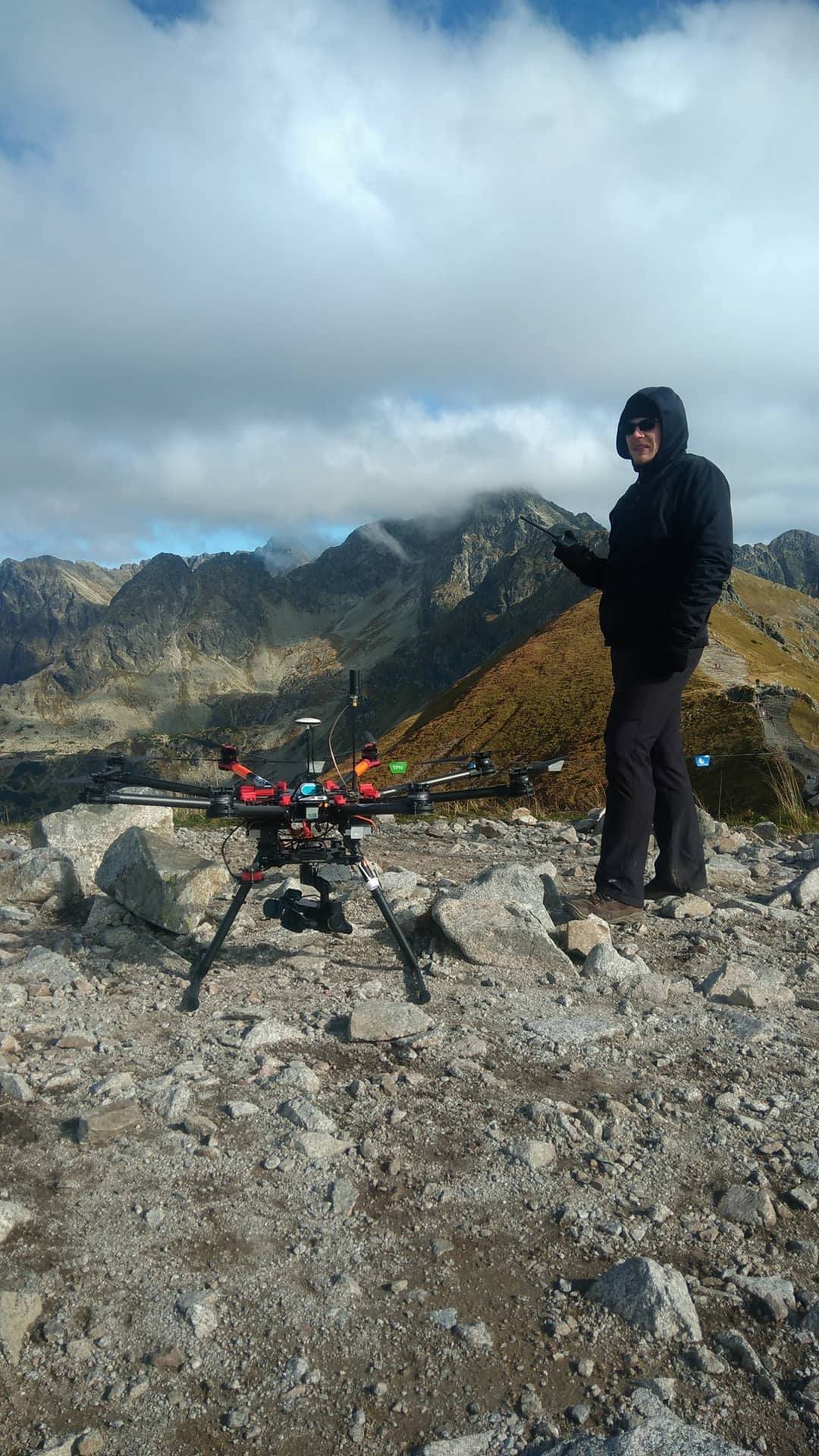
Assessment of the possibility of using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for the documentation of hiking trails in alpine areas
Paweł ĆWIĄKAŁA, Rafał KOCIERZ, Edyta PUNIACH, Michał NĘDZKA, Karolina Mamczarz, Witold NIEWIEM, Paweł WIĄCEK
The research described in this paper deals with the documentation of hiking trails in alpine areas. The study presents a novel research topic, applying up-to-date survey techniques and top quality equipment with practical applications in nature conservation. The research presents the initial part of the process—capturing imagery, photogrammetric processing, quality checking, and a discussion on possibilities of the further data analysis. The research described in this article was conducted in the Tatra National Park (TNP) in Poland, which is considered as one of the most-visited national parks in Europe. The exceptional popularity of this place is responsible for intensification of morphogenetic processes, resulting in the development of numerous forms of erosion. This article presents the outcomes of research, whose purpose was to verify the usability of UAVs to check the condition of hiking trails in alpine areas. An octocopter equipped with a non-metric camera was used for measurements. Unlike traditional methods of measuring landscape features, such a solution facilitates acquisition of quasi-continuous data that has uniform resolution throughout the study area and high spatial accuracy. It is also a relatively cheap technology, which is its main advantage over equally popular laser scanning. The paper presents the complete methodology of data acquisition in harsh conditions and demanding locations of hiking trails on steep Tatra slopes. The paper also describes stages that lead to the elaboration of basic photogrammetric products relying on structure from motion (SfM) technology and evaluates the accuracy of the materials obtained. Finally, it shows the applicability of the prepared products to the evaluation of the spatial reach and intensity of erosion along hiking trails, and to the study of plant succession or tree stand condition in the area located next to hiking trails.


AGH UST
2018
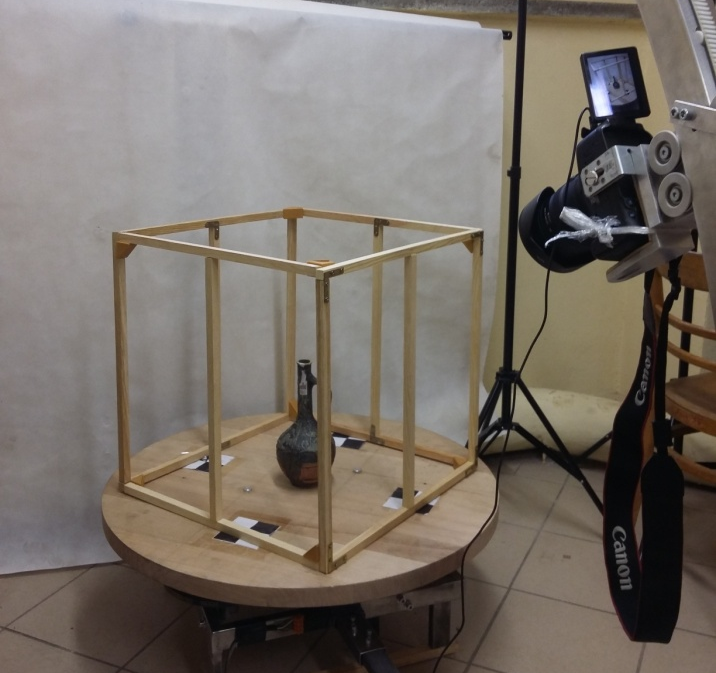
Automatic photography device FocusSphere for micro-close-range photogrammetry
Witold NIEWIEM
The paper presents basic construction principles of a new, original device called FocusSphere. The device is used to acquire photographic data and their geometrical properties for the purpose of close range photogrammetry. First of all, the paper shows how micro close range photogrammetry is successfully used in many areas. Subsequently, the construction of the device is briefly presented. The most important features and their influence for obtained results are discussed. The paper portrays also the process of determining the orientation of images for any FocusSphere program. For this purpose total station and photogrammetric measurements are made. The results of the measurements are analysed due to determine movements characteristics of the machine. Finally, the paper depicts main similarities and differences between FocusSphere and existing, conterminous technologies. The advantages and disadvantages of each solution are discussed.

AGH UST
2018
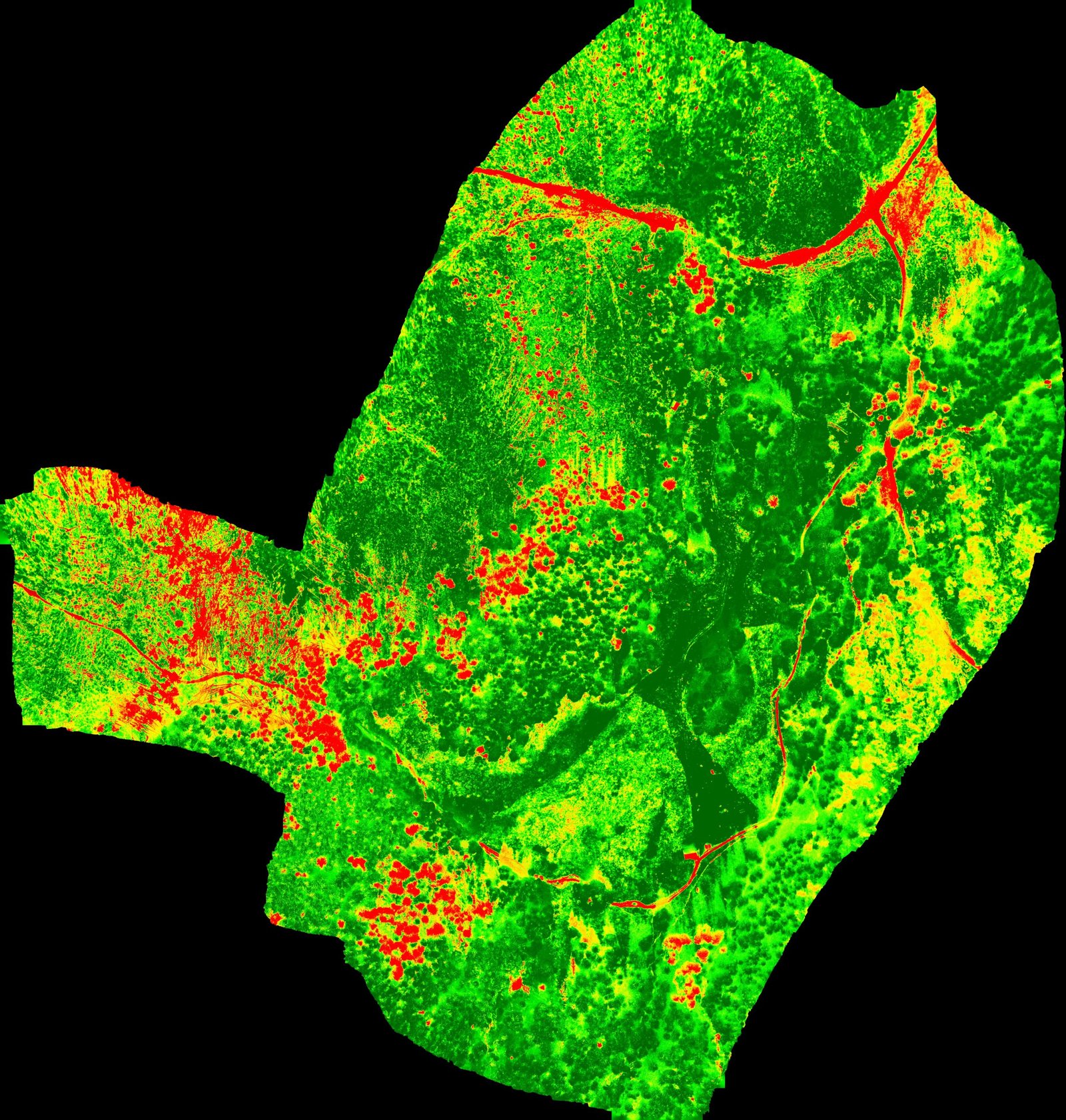
Assessment of the usefulness of unmanned aerial vehicles to inspection of erosive processes along tourist trails in terms of geomorphological mapping
Paweł ĆWIĄKAŁA, Rafał KOCIERZ, Edyta PUNIACH, Stanisław SZOMBARA, Michał NĘDZKA, Dawid MROCHEŃ, Witold NIEWIEM, Paweł WIĄCEK
The research described in this paper deals with the documentation of hiking trails in alpine areas. The study presents a novel research topic, applying up-to-date survey techniques and top quality equipment with practical applications in nature conservation. The research presents the initial part of the process-capturing imagery, photogrammetric processing, quality checking, and a discussion on possibilities of the further data analysis. The research described in this article was conducted in the Tatra National Park (TNP) in Poland, which is considered as one of the most-visited national parks in Europe. The exceptional popularity of this place is responsible for intensification of morphogenetic processes, resulting in the development of numerous forms of erosion. This article presents the outcomes of research, whose purpose was to verify the usability of UAVs to check the condition of hiking trails in alpine areas. An octocopter equipped with a non-metric camera was used for measurements. Unlike traditional methods of measuring landscape features, such a solution facilitates acquisition of quasi-continuous data that has uniform resolution throughout the study area and high spatial accuracy. It is also a relatively cheap technology, which is its main advantage over equally popular laser scanning. The paper presents the complete methodology of data acquisition in harsh conditions and demanding locations of hiking trails on steep Tatra slopes. The paper also describes stages that lead to the elaboration of basic photogrammetric products relying on structure from motion (SfM) technology and evaluates the accuracy of the materials obtained. Finally, it shows the applicability of the prepared products to the evaluation of the spatial reach and intensity of erosion along hiking trails, and to the study of plant succession or tree stand condition in the area located next to hiking trails.


AGH UST
2019
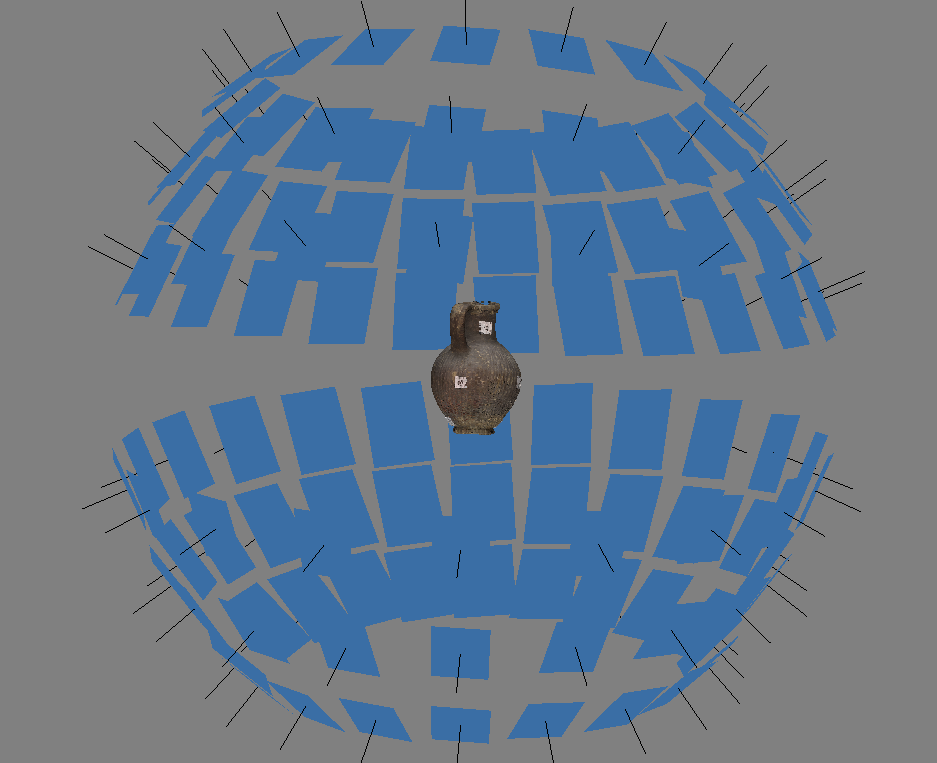
3D documentation of ceramic vessels with the use of modern measurement technologies
Edyta PUNIACH, Paweł ĆWIĄKAŁA, Mateusz BORUCHOWSKI, Witold NIEWIEM, Kamila NOCOŃ
Digital photogrammetry is quickly becoming a standard documentation tool in archaeology. Photogrammetric techniques are used to document both the findings of an archaeological site and the whole excavation. This paper is focused on a method of recording and documenting the surface of small objects by means of automatic photography device called FocusSphere. It is an original, inexpensive device prototype developed for the purpose of such a documentation. Resolution of 3D models obtained using FocusSphere is up to 0,1 mm depending on a non-metric camera and a lens which were used. Design and principle of operation of the device are presented in the paper. However, the main goal of the study was the assessment of FocusSphere suitability for the documentation of ancient ceramic vessels belonging to the Cypriot and Greek cultural circle. The research work was carried out in two stages. The first stage was to determine repeatability and accuracy of FocusSphere (ability to achieve repetition of the same position and ability to achieve desired position). For this purpose, precise measuring instrument (laser tracker) was used. The documentation of selected ceramic vessels differing in shape and surface characteristics was carried out in the second stage of the research. In order to assess the accuracy of the 3D models obtained by photogrammetric method the reference data were collected. They were cross sections of vessels measured by means of metrological device (measuring arm) guaranteeing the measurement accuracy at the sub-millimeter level. The results obtained were also compared with classic archaeological drawings. The methods of development of data collected by two different techniques (FocusSphere, measuring arm) along with indication of their advantages and disadvantages were finally discussed.

AGH UST
2018
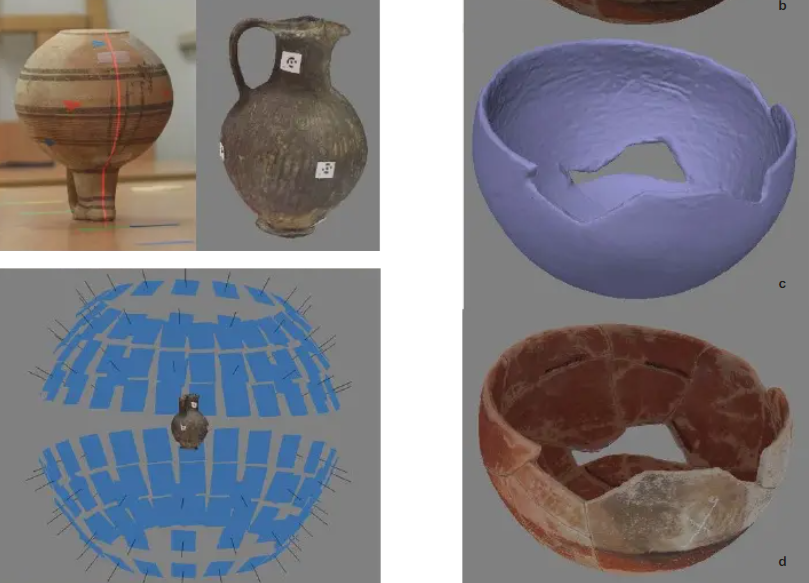
Photogrammetric Documentation of Ceramic Vessels in Ewdoksia Papuci-Władyka (ed.) MYSTERY OF THE CITY OF APHRODITE Archaeological heritage versus new technologies
Edyta PUNIACH, Paweł ĆWIĄKAŁA, Mateusz BORUCHOWSKI, Witold NIEWIEM, Kamila NOCOŃ, Małgorzata KAJZER
Digital photogrammetry is quickly becoming a standard documentation tool in archaeology. Photogrammetric techniques are used to document both the findings of an archaeological site and the whole excavation. This paper is focused on a method of recording and documenting the surface of small objects by means of automatic photography device called FocusSphere. It is an original, inexpensive device prototype developed for the purpose of such a documentation. Resolution of 3D models obtained using FocusSphere is up to 0,1 mm depending on a non-metric camera and a lens which were used. Design and principle of operation of the device are presented in the paper. However, the main goal of the study was the assessment of FocusSphere suitability for the documentation of ancient ceramic vessels belonging to the Cypriot and Greek cultural circle. The research work was carried out in two stages. The first stage was to determine repeatability and accuracy of FocusSphere (ability to achieve repetition of the same position and ability to achieve desired position). For this purpose, precise measuring instrument (laser tracker) was used. The documentation of selected ceramic vessels differing in shape and surface characteristics was carried out in the second stage of the research. In order to assess the accuracy of the 3D models obtained by photogrammetric method the reference data were collected. They were cross sections of vessels measured by means of metrological device (measuring arm) guaranteeing the measurement accuracy at the sub-millimeter level. The results obtained were also compared with classic archaeological drawings. The methods of development of data collected by two different techniques (FocusSphere, measuring arm) along with indication of their advantages and disadvantages were finally discussed.


AGH UST
2020
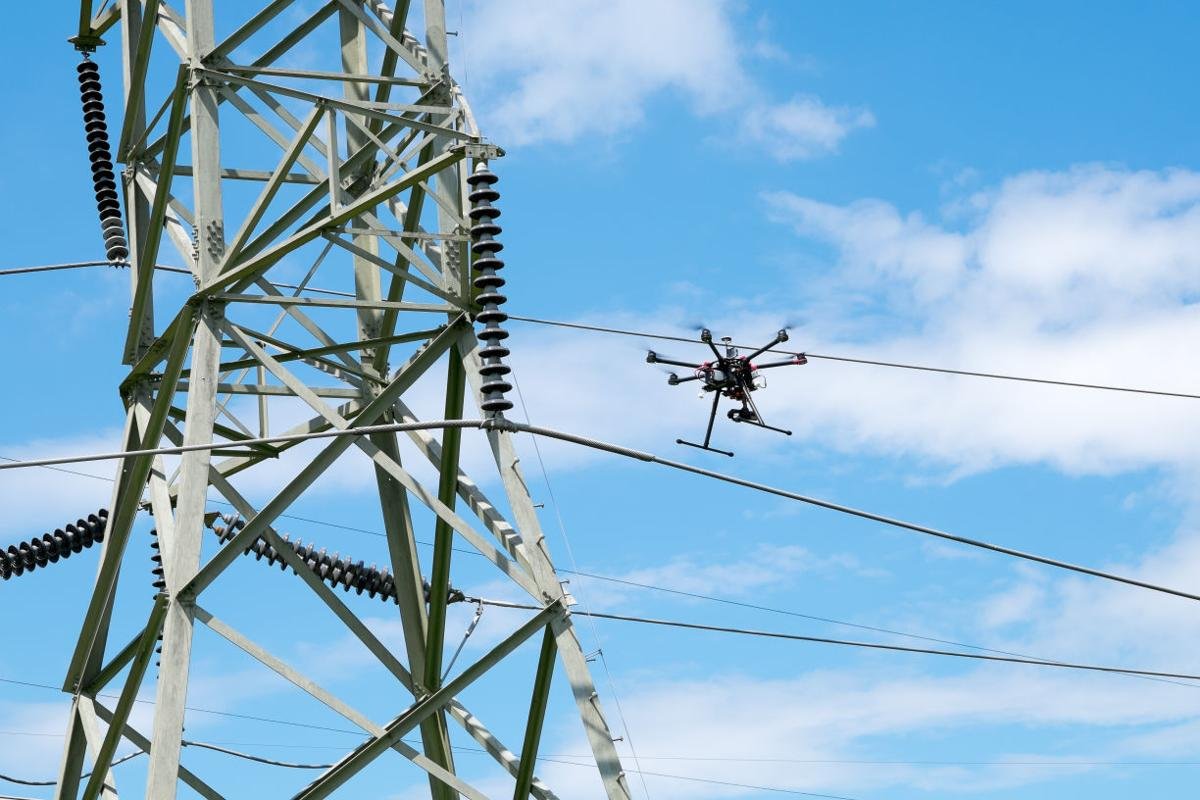
3D Reconstruction of Power Lines Using UAV Images to Monitor Corridor Clearance
Elżbieta Pastucha; Edyta Puniach; Agnieszka Ścisłowicz; Paweł Ćwiąkała; Witold Niewiem; Paweł Wiącek;
Regular power line inspections are essential to ensure the reliability of electricity supply. The inspections of overground power submission lines include corridor clearance monitoring and fault identification. The power lines corridor is a three-dimensional space around power cables defined by a set distance. Any obstacles breaching this space should be detected, as they potentially threaten the safety of the infrastructure. Corridor clearance monitoring is usually performed either by a labor-intensive total station survey (TS), terrestrial laser scanning (TLS), or expensive airborne laser scanning (ALS) from a plane or a helicopter. This paper proposes a method that uses unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images to monitor corridor clearance. To maintain the adequate accuracy of the relative position of wires in regard to surrounding obstacles, the same data were used both to reconstruct a point cloud representation of a digital surface model (DSM) and a 3D power line. The proposed algorithm detects power lines in a series of images using decorrelation stretch for initial image processing, the modified Prewitt filter for edge enhancement, random sample consensus (RANSAC) with additional parameters for line fitting, and epipolar geometry for 3D reconstruction. DSM points intruding into the corridor are then detected by calculating the spatial distance between a reconstructed power line and the DSM point cloud representation. Problematic objects are localized by segmenting points into voxels and then subsequent clusterization. The processing results were compared to the results of two verification methods—TS and TLS. The comparison results show that the proposed method can be used to survey power lines with an accuracy consistent with that of classical measurements.